Explore Your Patrilineal Ancestry with Y-DNA in Gramps Web
Gramps Web continues to expand its genealogy tools, and the latest release 25.9 introduces a milestone: Y-DNA visualization. For the first time in an open-source genealogy system, you can explore your paternal lineage directly within Gramps Web, and this feature is now live on Grampshub.
Understanding Y-DNA and What It Can Tell You
The Y chromosome is passed almost unchanged from father to son, which makes it a unique window into patrilineal ancestry. Mutations along the Y chromosome, called single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), accumulate over generations. By analyzing which SNPs are present or absent, it is possible to determine a person’s haplogroup – a branch on the human Y-chromosome tree that can trace back tens of thousands of years.
Haplogroups are associated with ancient migrations and population histories. For example, certain haplogroups are linked to the spread of early farmers into Europe, while others trace back to nomadic tribes of Central Asia or Africa. By identifying your Y-DNA haplogroup, you can place your paternal line within these broader historical patterns and see how your male ancestors may have moved across the globe over millennia.
How It Works in Gramps Web
To use the Y-DNA view, you need Y-DNA SNP data from a genetic testing service. This data is stored as a custom person attribute in your Gramps database. Gramps Web then uses the open-source yclade library and a local copy of the YFull human Y-chromosome tree to determine your most likely haplogroup.
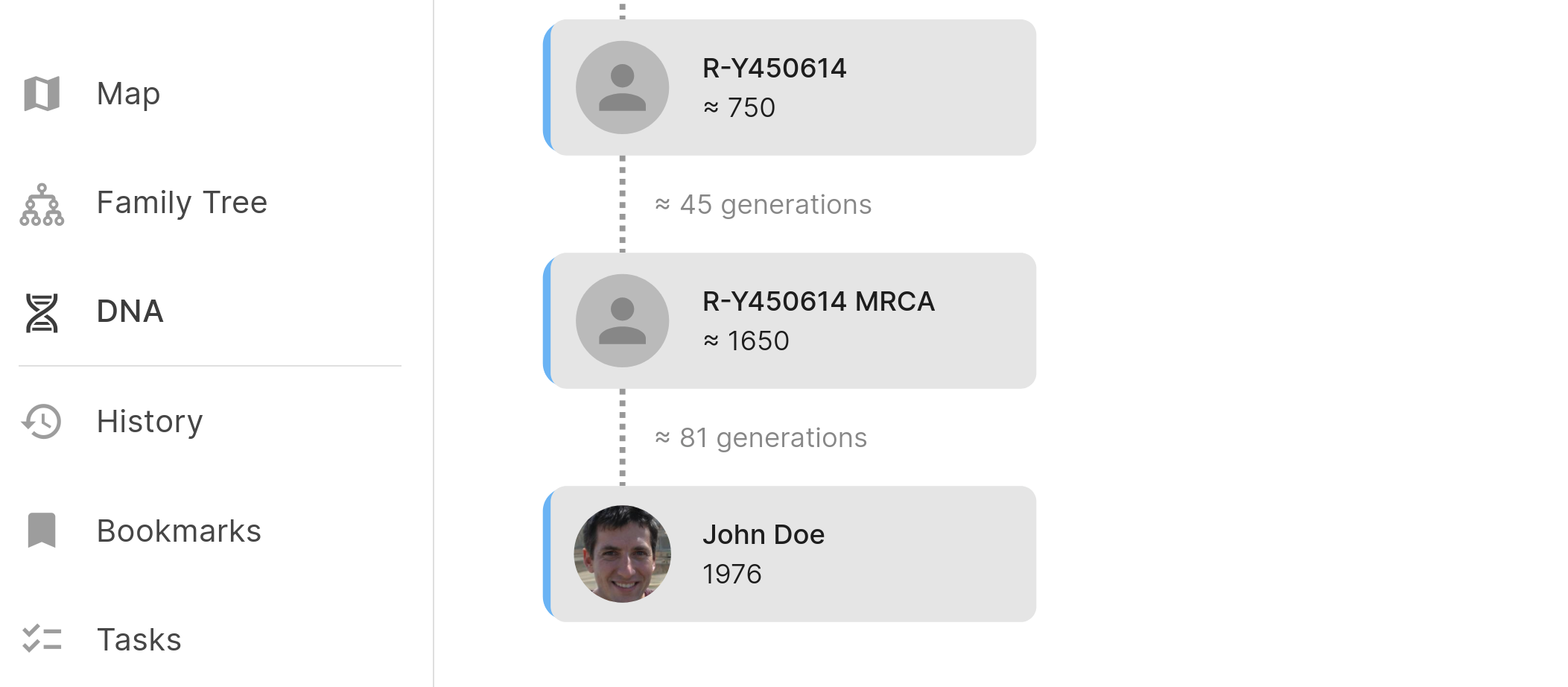
The resulting visualization shows a succession of ancestors, from the Y-chromosomal “Adam” to the most derived clade that matches your SNPs. Each node in the tree includes estimated dates, offering a rough timeline of your patrilineal lineage. The result is an interactive timeline of your paternal ancestry, showing successive male ancestors over thousands of years.
All analysis is performed locally within your Gramps database, so your Y-DNA data remains under your control while you explore your patrilineal ancestry.
For details on how to add your Y-DNA data, see the Gramps Web documentation.